PFAS Treatment in Groundwater
PFAS Treatment in Groundwater
Blog Article
Your Guide to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Conveniences
The frequency of PFAS contamination in water sources demands a comprehensive understanding of readily available therapy technologies. Each technology not only targets certain PFAS compounds however likewise plays a crucial role in boosting general water top quality and securing ecological honesty.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
Understanding PFAS contamination is essential for resolving its pervasive effect on environmental and human wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a team of artificial chemicals extensively made use of in numerous industrial and customer items because of their water- and grease-resistant homes. Generally discovered in firefighting foams, non-stick pots and pans, and water-repellent fabrics, PFAS have actually gotten in the environment through manufacturing procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from land fills
As soon as released, these materials continue the setting, causing prevalent contamination of soil and water sources. Their special chemical structure, defined by solid carbon-fluorine bonds, renders them resistant to destruction, causing a phenomenon called "forever chemicals." PFAS can collect in the human body and the food chain, potentially causing adverse health impacts, including immune system disruption, developing problems, and an increased threat of particular cancers.
Regulative agencies and health organizations are significantly identifying the relevance of PFAS contamination, motivating initiatives to keep an eye on, assess, and minimize its impacts. Comprehending the pathways of PFAS contamination is important for notifying public law and creating reliable methods to protect both environmental and human wellness.
Summary of Treatment Technologies
Different therapy technologies have been created to attend to the challenges posed by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These technologies can be broadly categorized into several groups, each with its special mechanisms and performance in eliminating PFAS substances.
One noticeable technique is ion exchange, which utilizes material materials to record and eliminate PFAS from polluted water. This approach is especially effective for short-chain PFAS and can attain significant decreases in concentration levels. One more innovation, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), utilizes solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to damage down PFAS into less hazardous materials. AOPs appropriate for dealing with a wide variety of PFAS substances but might need mindful optimization to make best use of efficacy.

Triggered Carbon Filtering
Activated carbon filtering is a commonly utilized technique for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water, known for its capability to adsorb a wide variety of natural substances. This modern technology utilizes activated carbon, an extremely permeable product with a substantial surface area, which assists in the binding of PFAS particles via physical adsorption. The effectiveness of activated carbon in removing PFAS is influenced by a number of elements, consisting of the type of carbon used, the contact time, and the concentration of PFAS in the water.
One of the benefits of activated carbon filtering is its versatility; it can be executed in different setups, such as granular activated carbon (GAC) systems or powdered triggered carbon (PAC) systems. GAC systems are commonly used in larger-scale applications, while special-interest group can be utilized in smaller or short-lived arrangements. Additionally, the technology is fairly easy to operate and preserve, making it obtainable for many water therapy centers.
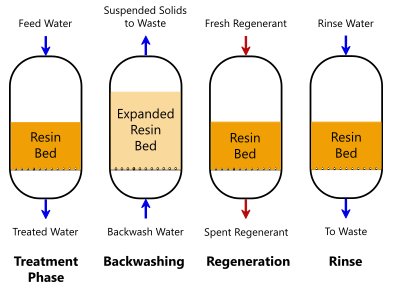
Ion Exchange Solution
Ion exchange systems stand for an additional efficient approach for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, enhancing approaches like turned on carbon filtering. These systems run on the concept of exchanging ions in the water with ions held on a resin product. Ion exchange materials can be especially formulated to target the negatively billed PFAS substances, successfully capturing them and enabling cleaner water to travel through.
One of the key advantages of ion exchange systems is their capacity to remove a vast range of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variants. This convenience makes them appropriate for numerous applications, ranging from local water therapy to industrial processes. In addition, ion exchange systems can typically achieve lower discovery restrictions for PFAS compared to a few other therapy approaches, therefore improving water quality.
Nonetheless, it is important to check and manage the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the performance can decrease in time as a result of saturation. Correct maintenance and replacement of the material are essential for maintaining the system's performance. In general, ion exchange systems supply a reliable and efficient option for PFAS elimination, adding significantly to safe drinking water requirements and ecological security.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) make use of effective oxidants to successfully break down PFAS substances in polluted water. These ingenious therapy techniques produce extremely responsive varieties, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down intricate PFAS particles into less dangerous by-products. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs generally employ combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, improving the oxidation potential and boosting destruction performance
The main advantage of AOPs hinges on their capability to target a broad variety of PFAS substances, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variations. This adaptability is necessary, as PFAS contamination commonly involves mixes of various compounds with varying chemical structures. AOPs use this link can be integrated right into existing water therapy systems, making them a useful solution for lots of towns and markets.
However, the execution of AOPs can be resource-intensive, needing careful factor to consider of operational prices and energy intake. Additionally, while AOPs are anchor reliable in breaking down PFAS, they might not entirely eliminate all byproducts, necessitating additional treatment actions - m270 pfas treatment. Generally, AOPs represent an appealing avenue for resolving PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water sources and enhanced public wellness protection

Conclusion
In final thought, dealing with PFAS contamination requires a comprehensive understanding of readily available therapy innovations. Turned on carbon purification, ion exchange systems, and advanced oxidation processes each existing distinct advantages for properly eliminating these damaging compounds from water resources. By choosing the suitable technology, areas can improve water quality, shield public wellness, and reduce the ecological dangers related to PFAS direct exposure. Continued study and application of these methods are necessary for efficient administration of PFAS contamination in influenced areas.
Report this page